Quick highlights1,2
- Treatment with SKYCLARYS resulted in lower modified Friedreich Ataxia Rating Scale (mFARS) scores, or less physical impairment, relative to placebo at week 48 in the pivotal MOXIe trial
- Lower mFARS scores were observed in patients treated with SKYCLARYS after 3 years relative to a matched set of untreated patients from a natural history study*
These exploratory analyses should be interpreted cautiously given the limitations of data collected outside of a controlled study, which may be subject to confounding.

MOXIe trial
SKYCLARYS was studied in the MOXIe trial, the largest FA study of its kind1,2
Designed in consultation with clinical specialists and patient advocacy groups. The MOXIe trial was an international, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter, registrational phase 2 trial. A total of 103 patients were randomized in a ratio of 1:1 to receive SKYCLARYS 150 mg once daily (n=51) or placebo (n=52).


measured the change from baseline in the mFARS scores of patients after 48 weeks of treatment with SKYCLARYS vs placebo.†2
†In the full analysis population of patients without pes cavus (n=82).
SKYCLARYS slowed FA disease progression in the pivotal MOXIe trial1
Treatment with SKYCLARYS resulted in less physical impairment relative to placebo at week 48.

ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adverse reactions reported in 10% or more of patients and greater than placebo were elevated liver enzymes (AST/ALT), headache, nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, oropharyngeal pain, influenza, vomiting, muscle spasms, back pain, decreased appetite, rash
Consistent results with SKYCLARYS1,2,12
Results from patient subgroups numerically favored SKYCLARYS over placebo:
- Age (±18 years)
- Sex
- GAA repeat length (≥675)
- Ambulatory status
- Pes cavus
All 4 components of the mFARS assessment numerically favored SKYCLARYS over placebo.
Bulbar function

Lower limb coordination

Upper limb coordination

Upright stability

In adolescent patients aged 16 to 18 years treated with SKYCLARYS, a group difference of -4.21 points versus placebo was observed at week 48.‡
The MOXIe trial was not powered to detect a statistically significant difference among subgroups.

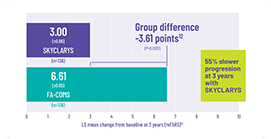
3-Year Post Hoc Propensity-Matched Analysis: Lower mFARS scores were observed relative to a matched set of untreated patients from a natural history study1
These exploratory analyses should be interpreted cautiously given the limitations of data collected outside of a controlled study, which may be subject to confounding.
Propensity matching is a method of comparing patients from a clinical trial with an external control by identifying comparable prognostic characteristics. It is informative in cases where a very long follow-up period is required to assess outcomes or when it is difficult to perform randomized controlled trials, such as in certain special patient populations.
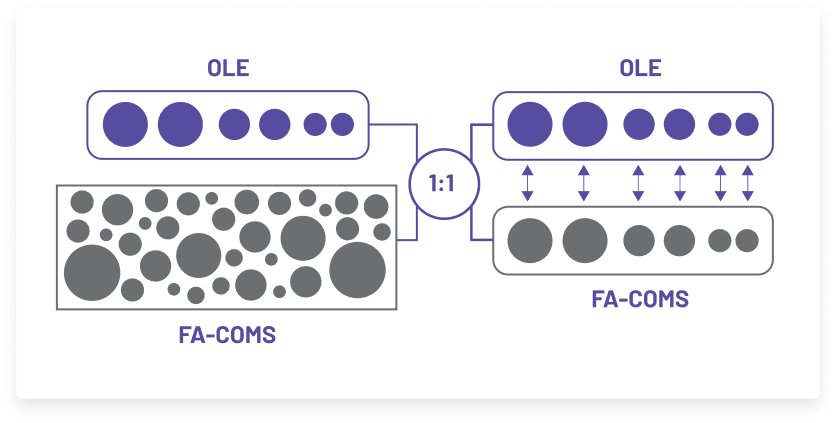
A post hoc propensity-matched analysis compared patients in the MOXIe open-label extension (OLE) with untreated patients who participated in a natural history study, the Friedreich Ataxia Clinical Outcome Measures Study (FA‑COMS).
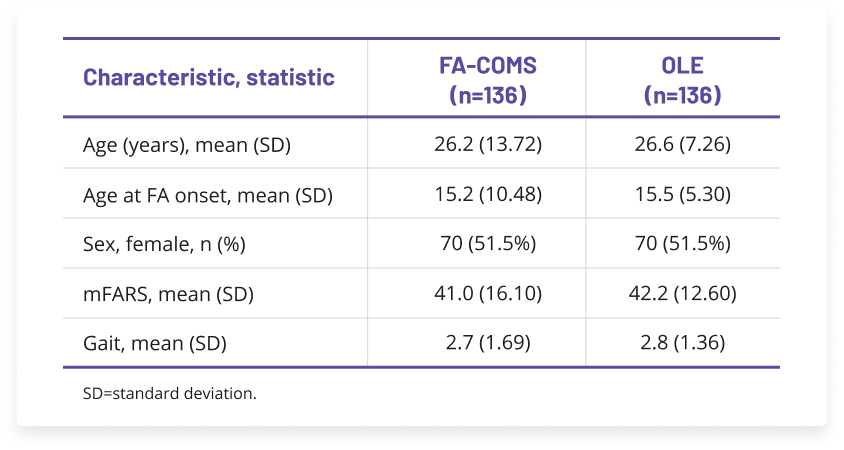
FA-COMS is a large, robust FA natural history study and has enrolled more than 1350 patients who have been followed for up to 15 years.

What is mFARS?2,6
The mFARS is a clinically validated neurological assessment that provides a detailed evaluation of a patient’s status and is generally accepted as a clinical trial endpoint due to its correlation with disease progression. mFARS is not required to be used in the clinic in order to treat with SKYCLARYS.
A higher score is associated with more severe disease.2,6
The mFARS is made up of 4 sections focused on functional abilities6:
Ability to complete many activities of daily living, such as getting dressed and eating
Predictor of time to loss of ambulation; the average score where loss of ambulation occurs is 65. A 2-point change in upright stability score may mean the difference between standing without support for 60 vs 30 seconds, or walking with mild vs severe impairment
Closely correlated with upright stability in predicting the likely rate of disease progression
Ability to speak clearly
While there is variability in progression, a patient’s mFARS score will worsen (increase) by about 2 points per year on average7
Patients with a younger age of onset may progress faster, worsening by an average of ~4 points per year.

SKYCLARYS was not evaluated in patients younger than 16 years or older than 40 years of age.

References:
1. Skyclarys. Prescribing Information. Reata Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2023.
2. Lynch DR, Chin MP, Delatycki
MB, et al. Safety and efficacy of omaveloxolone in Friedreich ataxia (MOXIe study). Ann Neurol.
2021;89(2):212-225. 3. Parkinson MH, Boesch S, Nachbauer W, Mariotti C, Giunti P. Clinical
features of
Friedreich’s ataxia: classical and atypical phenotypes. J Neurochem. 2013;126(suppl 1):103-117. 4.
Schulz
JB, Boesch S, Bürk K, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Friedreich ataxia: a European perspective. Nat
Rev
Neurol. 2009;5(4):222-234. 5. Rummey C, Farmer JM, Lynch DR. Predictors of loss of
ambulation in
Friedreich’s ataxia. EClinical Medicine. 2020;18:1-9. 6. Rummey C, Corben LA,
Delatycki MB, et al.
Psychometric properties of the Friedreich Ataxia Rating Scale. Neurol Genet. 2019;5(6):371.
7. Patel M,
Isaacs CJ, Seyer L, et al. Progression of Friedreich ataxia: quantitative characterization over 5 years.
Ann
Clin Transl Neurol. 2016;3(9):684-694. 8. Lynch DR, Chin MP, Boesch S, et al.
Efficacy of omaveloxolone in
Friedreich’s ataxia: delayed-start analysis of the MOXIe extension. Mov Disord. Published online
November
29, 2022. doi://10.1002/mds.29286 9. Galea CA, Huq A, Lockhart PJ, et al. Compound
heterozygous FXN
mutations and clinical outcome in Friedreich ataxia. Ann Neurol. 2016;79(3):485-495.
10. Fogel BL, Perlman
S. Clinical features and molecular genetics of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxias. Lancet
Neurol.
2007;6(3):245-257. 11. Wallace SE, Bird TD. Molecular genetic testing for hereditary
ataxia: what every
neurologist should know. Neurol Clin Pract. 2018;8(1):27-32. 12. Lynch DR,
Goldsberry A, Rummey C, et al.
Direct utility of natural history data in analysis of clinical trials: propensity match-based analysis of
omaveloxolone in Friedreich ataxia using the FA-COMS dataset. Preprint. Posted online August 16, 2022.
medRxiv 2022.08.12.22278684. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.12.22278684 13.
Beaulieu-Jones BK,
Finlayson SG, Yuan W, et al. Examining the use of real-world evidence in the regulatory process. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 2020;107(4):843-852.